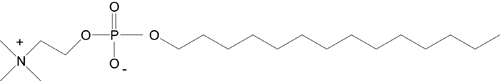
構造タンパク質
|
| CRTAP (E-1) |
Ms, Hu |
171-255 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393136 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| emerin (H-7) |
Ms, Rt, Hu |
195-224 (Ms) |
mouse IgG2a |
sc-393247 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| KIF17 (B-2) |
Hu |
324-359 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393253 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| Sarcospan (E-2) |
Ms, Hu |
162-199 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393187 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
合成と分解
|
| ACAD-10 (F-11) |
Ms, Rt, Hu, Hs, Bov |
409-439 (Hu) |
mouse IgM |
sc-393248 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| ALDH1A2 (G-2) |
Ms, Rt, Hu, Hs, Ca, Bov, Av |
28-51 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393204 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| Aldolase B (C-11) |
Ms, Rt, Hu |
131-167 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393278 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| Atg16 (E-10) |
Hu |
15-70 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393274 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| BUP-1 (B-5) |
Hu |
164-384 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393221 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| COX6b1 (C-3) |
Hu |
31-80 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393233 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| CYP27A1 (D-12) |
Hu |
335-451 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393222 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| DMGDH (E-6) |
Ms, Rt, Hu, Hs, Ca, Bov |
449-483 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2b |
sc-393178 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| MAN1B1 (E-10) |
Hu |
471-657 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393145 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| mHMGCS (B-8) |
Ms, Hu |
419-488 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2a |
sc-393256 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| NDUFA5 (A-3) |
Hu |
1-116 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2a |
sc-393273 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| Osgep (H-3) |
Ms, Hu |
89-335 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393199 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| Pancreatic Lipase (G-11) |
Ms, Rt |
29-47 (Rt) |
mouse IgG2a |
sc-393158 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| PLC-XD1 (A-1) |
Ms, Rt, Hu, Hs, Bov |
42-59 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393244 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| Stim2 (G-3) |
Ms, Rt, Hu, Hs, Bov, Av |
52-73 (Hu) |
mouse IgM |
sc-393211 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| SUMO-2/3/4 (C-3) |
Hu |
1-95 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393144 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
神経生物学
|
| 3PGDH (B-3) |
Hu |
260-533 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2b |
sc-393283 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| ABAT (B-5) |
Ms, Rt, Hu |
59-219 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393142 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| CNTFRα (F-2) |
Ms, Rt, Hu |
331-360 (Rt) |
mouse IgM |
sc-393214 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| Myelin P2 (A-3) |
Ms, Hu |
18-56 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2b |
sc-393173 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| Neurexophilin-3 (B-11) |
Ms, Rt, Hu, Hs, Ca |
175-202 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2a |
sc-393156 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| NPY1-R (E-4) |
Ms, Hu |
181-271 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2a |
sc-393192 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| NTR1 (G-9) |
Hu |
181-310 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2b |
sc-393205 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| PrP (H-8) |
Hu |
1-253 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2a |
sc-393165 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| rabphilin-3A (D-6) |
Hu, Rt |
516-576 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2a |
sc-393197 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| UIP1 (C-2) |
Ms |
1-300 (Ms) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393259 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
輸送関連タンパク質
|
| AP-180 (B-10) |
Ms, Rt, Hu, Hs, Ca, Bov, Por, Av |
2-27 (Ms) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393266 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| ASCT1 (C-8) |
Hu |
112-171 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393157 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| copine I/II/III (E-8) |
Hu |
266-346 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393249 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| Endophilin B1 (A-9) |
Hu |
250-309 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393191 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| NIPSNAP1/2 (F-4) |
Ms, Rt, Hu, Hs, Ca, Bov, Por |
197-284 (Ms) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393201 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| REEP1 (A-8) |
Ms, Rt, Hu |
145-169 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393242 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| SCAMP1 (G-8) |
Ms, Hu |
23-93 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393236 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| Sec61α (G-2) |
Ms, Rt, Hu, Hs, Ca, Bov, Por, Av |
392-423 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393182 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
キナーゼとホスファターゼ
|
| βPIX (H-3) |
Ms, Rt, Hu, Ca, Bov |
618-646 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393184 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| ACP1α (A-2) |
Hu |
60-79 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2a |
sc-393280 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| BPNT1 (C-12) |
Ms, Rt, Hu |
64-89 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393185 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| PIPK II (D-3) |
Ms, Hu, Ca, Por |
2-27 (Hu) |
mouse IgM |
sc-393246 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| PIR1 (B-6) |
Ms, Rt, Hu, Por |
39-58 (Hu) |
mouse IgM |
sc-393220 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| PLEKHM3 (H-2) |
Ms, Rt, Hu, Hs, Ca, Bov, Av |
1-21 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2a |
sc-393150 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| PYK2 (E-3) |
Ms, Hu, Hs, Ca, Por |
980-1009 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393181 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| Rsk-1 (A-10) |
Ms, Rt, Hu, Mink, Hs, Ca, Bov, Por |
707-735 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393147 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| SIK2 (B-12) |
Hu |
656-726 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2a |
sc-393139 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
腫瘍抑制因子 / アポトーシス
|
| APIP (G-2) |
Hu |
171-242 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2a |
sc-393194 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| DFNA5 (G-9) |
Hu |
221-496 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2a |
sc-393162 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| DLEC1 (D-11) |
Ms, Rt, Hu |
320-349 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393183 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| GADD 45γ (B-1) |
Ms, Hu |
95-159 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2b |
sc-393261 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| granzyme M (C-12) |
Hu |
89-126 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2b |
sc-393155 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| MAGE-D4/MAGE-D4B (E-7) |
Hu |
23-310 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2b |
sc-393203 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| ML-IAP (E-3) |
Hu |
72-97 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393237 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| NRAGE (F-9) |
Ms, Rt, Hu, Ca, Por |
28-57 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2b |
sc-393291 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| Pdcd-2 (H-1) |
Hu |
259-344 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2a |
sc-393137 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| PTEN (F-1) |
Ms, Rt, Hu, Hs, Ca, Bov, Por, Av |
3-29 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393186 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| Rfp2 (E-6) |
Hu |
212-309 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2a |
sc-393257 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| SESN2 (D-4) |
Ms, Hu |
45-106 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393195 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
シグナル中間体
|
| 14-3-3 ε (F-3) |
Ms, Rt, Hu, Hs, Ca, Bov, Por, Av |
136-175 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393177 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| Arylsulfatase E (F-4) |
Hu |
513-534 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2b |
sc-393224 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| Ataxin-3 (C-5) |
Hu |
176-228 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393193 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| BAZ1A (D-5) |
Hu, Ca, Bov, Por |
8-33 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393164 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| Crk I/II (D-6) |
Ms, Rt, Hu, Hs, Ca, Bov, Por |
109-132 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393160 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| DcpS (A-12) |
Ms, Rt, Hu, Hs, Por |
97-124 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2b |
sc-393226 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| eIF3K (F-4) |
Hu, Hs, Ca, Bov, Por |
1-218 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2a |
sc-393234 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| FBXO11 (E-9) |
Ms, Rt, Hu, Hs, Ca, Bov, Por, Av |
90-109 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2b |
sc-393229 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| Fyb (H-3) |
Hu |
504-614 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393276 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| GLB1L2 (B-10) |
Hu |
609-634 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2b |
sc-393202 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| IRS-4 (C-4) |
Hu |
1208-1239 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393207 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| MAPKAP-1 (F-3) |
Hu, Hs, Bov |
151-450 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393166 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| MD-1 (H-12) |
Hu |
24-51 (Hu) |
mouse IgG3 |
sc-393238 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| MOB1A (G-7) |
Ms, Rt, Hu, Ca, Bov |
1-64 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393212 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| NUBPL (G-7) |
Hu |
140-163 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393245 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| Otospiralin (A-12) |
Ms |
1-89 (Ms) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393239 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| PDHA2 (B-3) |
Ms, Rt |
287-312 (Ms) |
mouse IgG2b |
sc-393219 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| Peroxin 1 (D-9) |
Hu |
601-798 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393174 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| Pinch-1 (B-8) |
Ms, Hu, Hs, Ca, Bov, Por, Av |
12-41 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393151 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| PRMT2 (B-11) |
Ms, Rt > Hu |
350-376 (Ms) |
mouse IgM |
sc-393254 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| Proteassemblin (B-1) |
Ms, Rt, Hu, Hs, Ca, Bov |
38-63 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2b |
sc-393267 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| Sec5 (F-7) |
Hu |
1-300 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393230 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| SEMA6D (A-8) |
Hu |
369-420 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2a |
sc-393258 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| SPRED1 (E-5) |
Hu |
135-246 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393198 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| T6BP (H-6) |
Hu |
387-471 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393143 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| TRIM (E-12) |
Ms, Hu |
11-197 (Ms) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393175 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| TTC30A/B (A-10) |
Hu |
330-523 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2b |
sc-393206 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| WDR1 (B-10) |
Ms, Hu |
425-606 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2a |
sc-393159 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| WSB1 (A-7) |
Hu, Hs, Ca, Bov, Por |
302-354 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2a |
sc-393200 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| ZPBP1 (F-12) |
Ms, Rt, Hu, Hs |
309-338 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2b |
sc-393152 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
細胞膜受容体
|
| Flk-1 (D-8) |
Ms, Rt, Hu, Hs, Ca, Bov, Por |
1282-1321 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393163 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| Flk-1 (F-10) |
Ms, Rt, Hu, Hs, Ca, Bov, Por |
1292-1321 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2b |
sc-393179 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| GPD1 (H-10) |
Ms, Hu |
300-349 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393161 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| IL-11Rα (H-3) |
Ms, Rt |
403-432 (Ms) |
mouse IgG2a |
sc-393227 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| IL-3/IL-5/GM-CSFRβ (F-12) |
Ms, Rt, Hu |
867-893 (Ms) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393281 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
転写因子
|
| ADAR2 (A-5) |
Hu |
281-370 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393272 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| CstF-50 (A-5) |
Ms, Hu, Hs, Ca, Bov, Por |
1-300 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393260 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| DaRS (H-3) |
Hu |
170-467 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393275 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| Dnmt3b (D-1) |
Hu |
27-54 (Hu) |
mouse IgG3 |
sc-393279 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| ENL (D-6) |
Hu |
131-188 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393196 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| HCF2 (C-6) |
Hu |
555-792 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393250 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| HCF2 (D-12) |
Hu |
555-792 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2b |
sc-393251 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| HELIC2 (G-9) |
Ms, Hu, Hs, Ca, Bov, Por, Av |
1-300 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393170 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| HMG-I/HMG-Y (D-12) |
Hu |
1-95 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2b |
sc-393213 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| ITF-2 (C-1) |
Ms, Rt, Hu |
254-285 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393255 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| Liprin α2 (C-10) |
Ms, Hu, Hs, Bov |
489-590 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2a |
sc-393292 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| LysRS (B-2) |
Ms, Rt, Hu, Hs |
473-522 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393180 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| Med30 (C-6) |
Hu |
1-178 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2a |
sc-393289 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| Med7 (E-4) |
Hu |
38-233 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393210 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| mrnp41 (H-3) |
Ms, Rt, Hu |
12-39 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2b |
sc-393252 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| PATZ1 (H-2) |
Hu, Hs, Ca, Bov |
1-300 (Hu) |
mouse IgG3 |
sc-393223 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| RPUSD3 (C-2) |
Hu, Ca |
92-119 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2a |
sc-393209 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| SCML2 (C-12) |
Hu |
561-597 (Hu) |
mouse IgM |
sc-393243 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| SCML2 (H-3) |
Hu |
551-592 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2a |
sc-393265 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| SMC1α (H-6) |
Ms, Rt, Hu, Hs, Ca, Bov, Por, Av |
1202-1233 (Hu) |
mouse IgG3 |
sc-393171 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| SMC5 (B-11) |
Hu |
901-1090 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2a |
sc-393282 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| SNAI 1 (E-10) |
Hu |
21-150 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393172 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| SRA (E-5) |
Ms, Rt |
1-220 (Ms) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393240 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| TAL1 (B-8) |
Hu, Ca |
272-331 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2a |
sc-393288 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| TAL1 (C-4) |
Hu, Ca |
272-331 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393287 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| TFIIIC102 (C-2) |
Ms, Hu |
126-413 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393235 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| Timeless (G-4) |
Ms, Hu |
1-300 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2a |
sc-393146 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
成長因子とホルモン
|
| EMAP II (A-4) |
Ms, Rt, Hu |
268-289 (Hu) |
mouse IgM |
sc-393228 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| Lutropin β (A-9) |
Ms, Rt |
61-103 (Ms) |
mouse IgG2b |
sc-393284 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| PAFAH1B2 (A-6) |
Ms, Rt, Hu, Hs, Ca, Bov, Por |
10-31 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2a |
sc-393216 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| PAFAH1B2 (E-9) |
Ms, Rt, Hu, Hs, Ca, Bov, Por |
10-31 (Hu) |
mouse IgM |
sc-393217 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| Plfr (F-8) |
Ms |
124-244 (Ms) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393277 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
リンパ球シグナル伝達
|
| CD3-γ (H-7) |
Ms, Rt, Hu |
151-180 (Hu) |
mouse IgG3 |
sc-393271 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| DOM3Z (B-12) |
Hu |
82-381 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2a |
sc-393141 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| DOM3Z (D-9) |
Ms, Hu |
82-381 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393167 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
GDP / GTP結合タンパク質
|
| ARAP1 (A-3) |
Ms, Hu |
809-928 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2b |
sc-393138 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| ARL9 (G-10) |
Ms |
51-78 (Ms) |
mouse IgM |
sc-393264 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| E-Ras (B-12) |
Ms |
186-227 (Ms) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393268 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| GTPBP9 (F-10) |
Hu, Hs, Ca, Bov, Por |
181-393 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2a |
sc-393231 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| Rab 18 (D-5) |
Ms, Hu, Hs, Bov, Por |
93-206 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393168 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| Rho GAP p190-B (G-11) |
Ms, Hu |
1091-1250 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2a |
sc-393241 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| Tiam1 (G-1) |
Ms, Hu |
1-300 (Hu) |
mouse IgM |
sc-393176 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
ホメオドメインタンパク質
|
| Nkx-3.1 (A-3) |
Hu |
1-50 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393190 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| PTF1 (A-3) |
Ms, Rt, Hu, Ca, Por |
291-328 (Hu) |
mouse IgM |
sc-393148 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
細胞接着タンパク質
|
| cadherin-16 (E-7) |
Ms |
1-300 (Ms) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393153 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| Integrin α3 (A-6) |
Hu |
841-872 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393290 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| Integrin β2 (H-7) |
Hu |
1-120 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393140 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| Laminin γ-2 (G-7) |
Ms, Rt, Hu, Hs, Ca, Bov |
1163-1190 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2a |
sc-393225 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| paxillin (C-10) |
Ms, Rt, Hu |
59-89 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393149 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
チャネルタンパク質
|
| GABAB R2 (E-4) |
Ms, Rt, Hu, Ca |
183-482 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393286 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| GABAB R2 (H-10) |
Ms, Rt, Hu, Ca |
183-482 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2a |
sc-393270 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| ROM-K (D-3) |
Ms, Rt, Hu |
321-390 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2a |
sc-393189 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
ステロイド受容体
|
| GR (G-5) |
Ms, Hu |
121-420 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2b |
sc-393232 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| Rev-erbα (E-12) |
Ms, Hu |
21-69 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393215 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
細胞周期タンパク質
|
| ASF1B (C-6) |
Hu |
1-202 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2b |
sc-393169 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| DHFR (C-4) |
Ms, Rt, Hu |
77-106 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2b |
sc-393154 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| MAD2 (C-9) |
Ms, Rt, Hu, Hs, Bov, Por |
178-205 (Hu) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393188 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| NVL (A-10) |
Hu |
405-482 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2a |
sc-393285 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| p-Cdk5 (C-7) |
Ms, Rt, Hu, Hs, Bov, Por |
142-171(Hu) |
mouse IgG3 |
sc-377558 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| PCTAIRE-3 (H-4) |
Ms |
11-69 (Ms) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393262 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
その他
|
| C9orf114 (H-7) |
Ms, Rt, Hu, Hs, Ca, Bov, Por |
78-99 (Hu) |
mouse IgG2a |
sc-393263 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |
| Ste7 (B-12) |
Saccharomyces cerevisiae |
2-24 (S) |
mouse IgG1 |
sc-393269 |
![e-Nacalai.jpg]() |