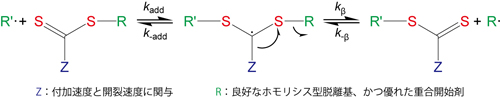
Polysciences社では生分解性高分子を販売しています。各種ポリマーに加えて、均一サイズの粒子タイプもラインアップしています。生分解性高分子は、ドラッグデリバリーの担体、縫合糸やインプラントの材料、土壌中で分解するプラスチックなどの研究に有用です。
※ 研究用ですので臨床用としては使用できません。
この製品に関するご意見・ご照会・お問合せはこちら
メーカー情報
Polysciences is pleased to offer a range of bio-erodable polymers for evaluation and product development. These materials find usefulness for studies involving bio-erodable drug matrices, biodegradable sutures and implant materials, as well as for situations requiring polymers which can biodegrade when placed in the soil.
● Biodegradable Particles
Biodegradable polymers & microspheres such as PLGA types are receiving high levels of interest for controlled release of active materials in the pharmaceutical industry as growth platforms (e.g. degradable scaffolds for implants and bone grafts) and as prototype materials to measure biodegradation kinetics under specific conditions.
As these sciences expand, there will be a need for controlled particle size biodegradable microspheres for calibration of instrumentation and for particle size assays.
Polysciences Inc. offers two PLGA polymer (50:50 and 75:25 Lactic Acid : Glycolic Acid) in three narrow sizes (75μm, 100μm and 120μm; 5-10% CVs). These highly uniform particle populations serve as excellent models for controlled degradation rate measurements, and for the development of prototype scaffolds or devices.
- Poly(Lactic Acid-co-Glycolic Acid) Uniform Dry Microspheres, 50:50 LA/GA, 100µm
- Poly(Lactic Acid-co-Glycolic Acid) Uniform Dry Microspheres, 50:50 LA/GA, 120µm
- Poly(Lactic Acid-co-Glycolic Acid) Uniform Dry Microspheres, 50:50 LA/GA, 75µm
- Poly(Lactic Acid-co-Glycolic Acid) Uniform Dry Microspheres, 75:25 LA/GA, 100µm
- Poly(Lactic Acid-co-Glycolic Acid) Uniform Dry Microspheres, 75:25 LA/GA, 120μm
- Poly(Lactic Acid-co-Glycolic Acid) Uniform Dry Microspheres, 75:25 LA/GA, 75μm
● Poly(dl-lactide/glycolide) Polymers
These copolymers are prepared for easier processability and for modified properties. Polysciences offers both l-lactide and dl-lactide copolymer in several ratios. Other ratios can be prepared on a custom basis.
● Poly(l-lactic acid) Polymers
This polymer has been widely used in sutures, implants and controlled release systems. It’s low molecular weights are for drug matrices, but its high molecular weights are for osteosynthesis (pins for bone repair). Poly(l-lactic acid) Kit (Cat. #18599) contains 5g each of 4 available polymers in the MW range of 2,000 to 300,000.
● Polycaprolactone-Polyethylene Glycol Polymers
There is increased interest in biodegradable polymers for both biomedical and industrial applications. Among the leading candidates for biodegradation are caprolactone based materials due to it's approved uses by the FDA for drug delivery systems, sutures, long term implants and adhesion barriers as well as new tissue scaffold host systems.
Caprolactone itself is a biodegradable polyester with a relatively low melting point (60C) but a glass transition temperature (Tg) around -60C. The high crystallinity in the polyester accounts for this property balance. It is made by metal catalyzed ring opening polymerization of epsilon caprolactone. A typical molecular weight of standard polycaprolactone homopolymer is 188k Daltons. By comparison, a 100% polylactic acid homopolymer with Mw 330k Daltons has a (Tg) temperature of +55C and a melting temperature, Tm of about 175C.
Further modifications of polycaprolactone are possible by converting it into diblock (A-B) or triblock (A-B-A) copolymers with polyethylene glycol. Synthetic methods which lead to block structures allow the polymer to have controlled biodegradation rates as well as improved physiological compatibility characteristics. Low molecular weight PEG blocks or caprolactone blocks are tolerated in the human body and are excretable. Such amphiphilic block copolymers are also convertible into polymersomes or vesicles which may contain active compounds (API) which are released during degradation.
ln addition to our full line of Polycaprolactone Diblock and Triblock Polymers, Polysciences, Inc. offers custom synthesis services for other compositions and block molecular weights. The numbers listed under the product indicate the approximate molecular weight of the block segments. The PEG terminal groups are blocked as methyl ethers but the caprolactone end groups are hydroxyl and are suitable for functionalization.
・Diblock Polymers
- PCL(1,000)-b-PEG(1,000), Diblock Polymer
- PCL(1,000)-b-PEG(2,000), Diblock Polymer
- PCL(1,000)-b-PEG(5,000), Diblock Polymer
- PCL(5,000)-b-PEG(1,000), Diblock Polymer
- PCL(5,000)-b-PEG(2,000), Diblock Polymer
- PCL(5,000)-b-PEG(5,000), Diblock Polymer
・Triblock Polymers
- PCL(1,000)-b-PEG(1,000)-b-PCL(1,000), Triblock Polymer
- PCL(1,000)-b-PEG(10,000)-b-PCL(1,000), Triblock Polymer
- PCL(1,000)-b-PEG(2,000)-b-PCL(1,000), Triblock Polymer
- PCL(1,000)-b-PEG(6,000)-b-PCL(1,000), Triblock Polymer
- PCL(5,000)-b-PEG(1,000)-b-PCL(5,000), Triblock Polymer
- PCL(5,000)-b-PEG(10,000)-b-PCL(5,000), Triblock Polymer
- PCL(5,000)-b-PEG(2,000)-b-PCL(5,000), Triblock Polymer
- PCL(5,000)-b-PEG(5,000)-b-PCL(5,000), Triblock Polymer
● Polylactic Acid-Polyethylene Glycol Polymers
Biodegradable Polymers based on copolymers of polylactic acid (PLA) and polyethylene glycol (PEG) offer scientists new tools for controlled release formulations and delivery platforms.
Polymer structures featuring polyethylene glycol (PEG), with biodegradable or biocompatabile segments offering micelluar, nano and microsphere morphologies which are useful for controlled release formulations. Molecular weights of blocks controlled by GPC. Alternative structures can be synthesized.
A new class of polymeric biomaterials is emerging. The biodegradability of polymers based on lactic acid(LA) and its copolymers with ethylene glycol (EG) opens up new avenues for drug delivery, gene therapy, tissue engineering and determination of cellular pathway mechanisms.
Historically there have been three basic building block monomers for degradable polymers: lactides, glycolides and caprolactone. All are in clinical use and show varying degrees of degradability based on backbone compositions, crystallinity and molecular weights.
Lactic acid is a “chiral” molecule having both (L) and (D) forms with (L) being the common metabolite. The family of lactic acid polymers includes the pure poly-L- lactic acid (L form of PLA), the pure poly-D-lactic acid and the poly-D, L lactic acid (DL-PLA). Many other useful compositions occur when the polymer is organized into diblocks with ethylene glycol and/or glycolic acid comonomers or triblocks with ethylene glycol and/or glycolic acid.
Polymers of this type are insoluble in water but degrade by hydrolytic attack on their ester bonds. This degradation can be mediated by selective choice of comonomers such as ethylene glycol which enhance the penetration of water and rate of hydrolysis.
・Diblock Polymers
- PEG(1,000)-b-PLA(5,000), Diblock Polymer
- PEG(1,000)-b-PLA(750), Diblock Polymer
- PEG(10,000)-b-PLA(5,000), Diblock Polymer
- PEG(350)-b-PLA(300), Diblock Polymer
- PEG(5,000)-b-PLA(1,000), Diblock Polymer
- PEG(5,000)-b-PLA(10,000), Diblock Polymer
- PEG(5,000)-b-PLA(5,000), Diblock Polymer
・Triblock Polymers
- PLA(1,000)-b-PEG(1,000)-b-PLA(1,000), Triblock Polymer
- PLA(1,000)-b-PEG(10,000)-b-PLA(1,000), Triblock Polymer
- PLA(1,000)-b-PEG(4,000)-b-PLA(1,000), Triblock Polymer
- PLA(10,000)-b-PEG(10,000)-b-PLA(10,000), Triblock Polymer
- PLA(2,000)-b-PEG(1,000)-b-PLA(2,000), Triblock Polymer
- PLA(5,000)-b-PEG(1,000)-b-PLA(5,000), Triblock Polymer
- PLA(5,000)-b-PEG(10,000)-b-PLA(5,000), Triblock Polymer
● Other Polymers
- Biodegradable Polymers Kit
- Glycolide, 99.9%
- Guar Gum
- Poly(dimethylsiloxane-b-ethylene oxide), methyl terminated
- Poly(dimethylsiloxane-b-ethylene oxide), methyl terminated
- Poly(dl-lactic acid) [MW ~ 20,000 - 30,000]
- Poly(dl-lactic acid) [MW 15,000]
- Poly(dl-lactic acid) i.v. 2.0 -2.8dl/g
- Poly(ethylene oxide-b-propylene oxide)
- Poly(ethylene oxide-b-propylene oxide) [ratio 0.15:1]
- Poly(ethylene oxide-b-propylene oxide) [ratio 0.33:1]
- Poly(ethylene oxide-b-propylene oxide) [ratio 0.8:1]
- Poly(ethylene oxide-b-propylene oxide) [ratio 3:1]
- Poly(glycolic acid) [i.v. 1.0-2.0]
- Poly(l-alanine)
- Poly(l-lactide/glycolide) [70:30]
- Poly(l-lactide/glycolide) [70:30]
- Poly[(-)3-hydroxybutyric acid]
- Poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate], MW ~ 10,000
- Poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate], MW ~ 1000
- Poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate], MW ~ 2000
- Poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate], MW ~ 3000
- Poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate], MW ~ 500
- Poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate], MW ~ 5000
- Polycaprolactam [MW ~ 18,000]
- Polycaprolactam [MW 35,000]
- Polycaprolactone
- Polycaprolactone diol [MW 1,250]
- Polycaprolactone diol [MW 2,000]
- Polycaprolactone, powdered
- Polycaprolactone-based Biodegradable Polymers
- Polyethylene-co-vinyl acetate 70:30 (wt) MW 55,000
- Polyethylene-co-vinyl acetate 70:30 (wt) MW 60,000
- Polylactic Acid and Polyethylene Glycol Based Biodegradable Polymers
- Pullulan, desalinized
この製品に関するご意見・ご照会・お問合せはこちら